Buying vs leasing a car worksheet – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of buying vs. leasing a car with our meticulously crafted worksheet. This invaluable tool empowers you with the knowledge and insights necessary to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals, lifestyle, and usage patterns.
Through a series of insightful sections, we delve into the intricacies of each option, examining upfront costs, ownership rights, long-term value, lifestyle considerations, and tax implications. Our objective analysis and practical guidance will equip you with the confidence to choose the path that best suits your individual circumstances.
Financial Considerations
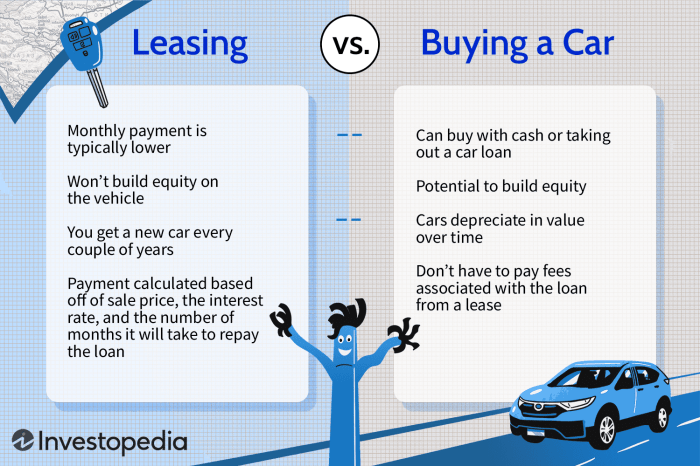
Financial considerations are crucial in determining the most suitable option between buying and leasing a car. Upfront costs, monthly payments, interest rates, and down payments play a significant role in shaping the financial burden associated with each option.
| Buying | Leasing | |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Costs | Down payment, taxes, registration fees | Down payment (usually lower than buying), security deposit |
| Monthly Payments | Loan payments (principal and interest) | Lease payments (cover depreciation, interest, maintenance) |
| Interest Rates | Typically higher than lease rates | Typically lower than loan rates |
| Down Payments | Typically higher than lease down payments | Typically lower than loan down payments |
Additionally, leasing involves mileage limits and excess wear and tear charges. Exceeding mileage limits can result in additional fees, while excessive wear and tear charges can be levied at the end of the lease term.
Ownership and Flexibility
Buying a car confers ownership rights, while leasing grants temporary usage rights. Ownership provides greater flexibility in terms of customization, modification, and resale. However, leasing offers more flexibility in upgrading or terminating the contract, making it suitable for those who prefer short-term commitments or anticipate changing vehicle needs.
For example, individuals who frequently need to upgrade their vehicles or prefer to drive the latest models may find leasing to be a more advantageous option due to its flexibility.
Long-Term Value
The long-term value of buying vs leasing a car depends on several factors, including resale value, depreciation, and maintenance costs.
| Buying | Leasing | |
|---|---|---|
| Resale Value | Can be higher than residual value (leased car’s estimated value at the end of the lease term) | Typically lower than resale value of purchased car |
| Depreciation | Car loses value over time | Lessee only pays for depreciation during the lease term |
| Maintenance Costs | Owner responsible for all maintenance and repair costs | Some maintenance costs may be covered by the lease contract |
Buying a car can provide potential long-term savings if the vehicle is well-maintained and retains its resale value. However, leasing may offer lower monthly payments and predictable maintenance costs, making it a more cost-effective option for some individuals.
Lifestyle and Usage
Lifestyle and usage patterns can significantly influence the decision between buying and leasing a car. Factors such as annual mileage, driving habits, and vehicle preferences should be carefully considered.
Individuals who drive high annual mileage may find buying a car more economical, as they can avoid mileage limits and excess wear and tear charges associated with leasing. On the other hand, those who drive less frequently or prefer to have access to the latest models may find leasing to be a more suitable option.
Tax Implications
Tax implications can vary depending on whether a car is bought or leased. Sales tax, property tax, and income tax deductions should be taken into account.
| Buying | Leasing | |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Tax | Paid upfront | Paid monthly or included in lease payments |
| Property Tax | Paid annually by the owner | Typically not applicable to leased vehicles |
| Income Tax Deductions | Interest on loan payments may be deductible | Lease payments may be partially deductible for business use |
Understanding the tax implications can help individuals make informed decisions about the most tax-efficient option for their circumstances.
FAQ Summary: Buying Vs Leasing A Car Worksheet
What are the key financial considerations when comparing buying vs. leasing?
Upfront costs, monthly payments, interest rates, down payments, mileage limits, and excess wear and tear charges are crucial financial factors to evaluate.
How does ownership differ between buying and leasing?
Buying grants you full ownership of the vehicle, while leasing provides temporary possession with limited ownership rights.
What are the potential tax implications of buying vs. leasing?
Sales tax, property tax, and income tax deductions vary depending on the option chosen and whether the vehicle is used for business or personal purposes.