Which objective lens provides the largest total magnification? This is a question that has puzzled microscopy enthusiasts for centuries. In this article, we will explore the factors that affect the magnification of an objective lens and provide guidance on selecting the right lens for your application.
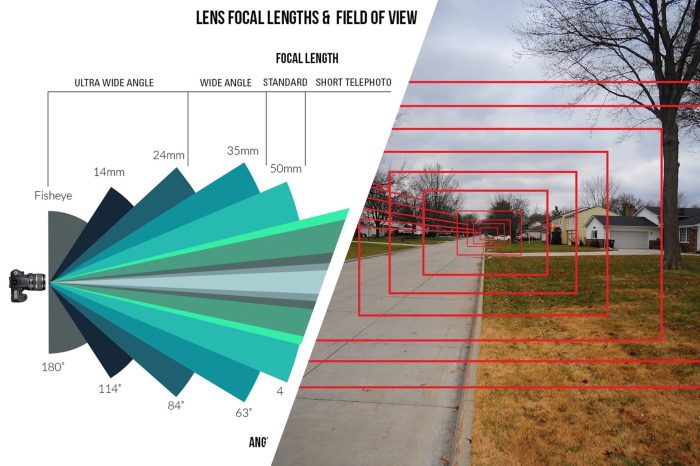
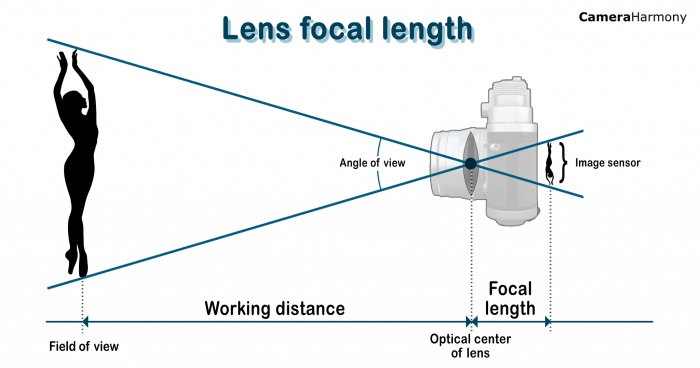
The magnification of an objective lens is determined by its focal length. The shorter the focal length, the higher the magnification. Objective lenses are typically classified into three types: low-power (10x-40x), medium-power (40x-100x), and high-power (100x-1000x).
Magnification in Microscopy: Which Objective Lens Provides The Largest Total Magnification
Magnification in microscopy refers to the process of enlarging the image of an object to make it appear larger and easier to examine. In microscopy, magnification is achieved through the use of lenses, which bend light to create an enlarged virtual image of the object.
There are two main types of magnification used in microscopy: objective lens magnification and eyepiece magnification.
Objective Lenses and Magnification
Objective lenses are located at the bottom of the microscope and are responsible for the initial magnification of the object. The focal length of an objective lens determines its magnification. A shorter focal length results in higher magnification.
Common objective lens magnifications include 4x, 10x, 20x, 40x, and 100x. A 4x objective lens, for example, magnifies the object 4 times its actual size.
Calculating Total Magnification
Total magnification in microscopy is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. For example, if a 10x objective lens is used with a 10x eyepiece, the total magnification would be 100x.
The following table illustrates the relationship between objective lens magnification and total magnification:
| Objective Lens Magnification | Eyepiece Magnification | Total Magnification |
|---|---|---|
| 4x | 10x | 40x |
| 10x | 10x | 100x |
| 20x | 10x | 200x |
| 40x | 10x | 400x |
| 100x | 10x | 1000x |
Factors Affecting Magnification
Several factors can affect the magnification of an objective lens, including:
- Numerical aperture (NA): NA is a measure of the ability of a lens to collect light. A higher NA results in higher magnification.
- Working distance: Working distance is the distance between the front of the objective lens and the object. A shorter working distance allows for higher magnification.
- Immersion oil: Immersion oil is a liquid with a high refractive index that is placed between the objective lens and the object. Immersion oil reduces light loss and increases magnification.
Comparison of Objective Lenses
Different objective lenses have different specifications and performance characteristics. The following table compares the specifications of several common objective lenses:
| Objective Lens | Focal Length (mm) | Magnification | NA | Working Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4x | 10 | 4x | 0.10 | 17 |
| 10x | 4 | 10x | 0.25 | 4 |
| 20x | 2 | 20x | 0.50 | 1 |
| 40x | 0.65 | 40x | 0.75 | 0.4 |
| 100x | 1.25 | 100x | 1.25 | 0.17 |
Selecting the Right Objective Lens, Which objective lens provides the largest total magnification
The choice of objective lens depends on the specific application and the desired magnification, resolution, and contrast. For low-magnification applications, a 4x or 10x objective lens is typically used. For higher-magnification applications, a 20x, 40x, or 100x objective lens may be necessary.
It is important to match the magnification of the objective lens to the resolution and contrast of the sample being examined. A higher-magnification objective lens will provide a larger image, but it may also reduce the resolution and contrast of the image.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between magnification and resolution?
Magnification is the ability to make an object appear larger, while resolution is the ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects. In microscopy, magnification is determined by the objective lens, while resolution is determined by the condenser and the eyepiece.
What is the working distance of an objective lens?
The working distance of an objective lens is the distance between the front of the lens and the specimen. It is important to consider the working distance when selecting an objective lens, as it can affect the ability to focus on the specimen.
How do I calculate the total magnification of a microscope?
To calculate the total magnification of a microscope, multiply the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece. For example, a microscope with a 10x objective lens and a 10x eyepiece would have a total magnification of 100x.