Falling objects drop with an average acceleration of 9.8m/s2, a fundamental concept in physics that has captivated scientists and engineers for centuries. This acceleration due to gravity governs the motion of all falling objects, regardless of their mass or shape, and has profound implications in diverse fields.
From the towering skyscrapers to the celestial dance of planets, understanding the acceleration of falling objects is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and precision in countless applications.
Acceleration of Falling Objects: Falling Objects Drop With An Average Acceleration Of 9.8m/s2
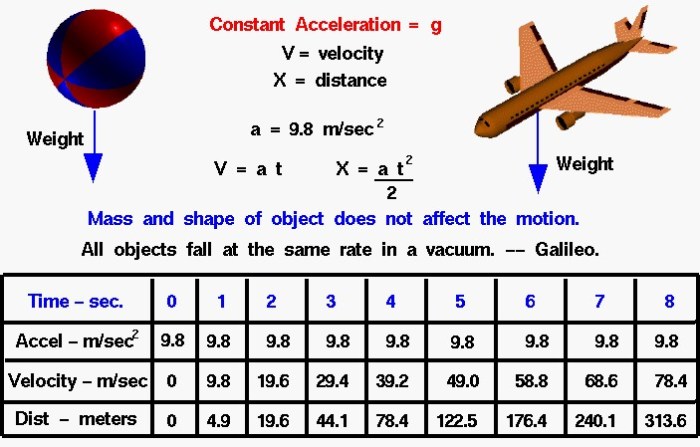
Falling objects accelerate towards the ground due to the force of gravity. This acceleration is constant and has a value of approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (9.8 m/s2). The acceleration due to gravity is often denoted by the symbol ‘g’.The
acceleration of a falling object is independent of its mass, shape, or size. This means that all objects fall at the same rate in a vacuum, regardless of their other properties. However, in the presence of air resistance, the acceleration of a falling object may be reduced.
Applications of Understanding Falling Object Acceleration, Falling objects drop with an average acceleration of 9.8m/s2
Understanding the acceleration of falling objects has many practical applications in engineering, construction, and sports. For example, engineers use the concept of acceleration to design bridges and buildings that can withstand the impact of falling objects. Construction workers use the concept of acceleration to calculate the safe height for scaffolding and other structures.
Athletes use the concept of acceleration to optimize their performance in sports such as high jump and long jump.
Experimental Verification of Falling Object Acceleration
The acceleration due to gravity can be verified experimentally using a simple experiment. The experiment involves dropping an object from a known height and measuring the time it takes for the object to fall. The acceleration due to gravity can then be calculated using the following formula:“`a = 2h / t^2“`where:* ‘a’ is the acceleration due to gravity (in m/s2)
- ‘h’ is the height from which the object was dropped (in meters)
- ‘t’ is the time it took for the object to fall (in seconds)
Historical Perspectives on Falling Object Acceleration
The understanding of falling object acceleration has evolved over time. In ancient times, philosophers such as Aristotle believed that heavier objects fall faster than lighter objects. However, in the 16th century, Galileo Galilei conducted experiments that showed that all objects fall at the same rate in a vacuum.
This discovery was later confirmed by Isaac Newton, who developed the laws of motion and universal gravitation.
Expert Answers
What factors influence the acceleration of falling objects?
Air resistance and object shape can affect the acceleration of falling objects, causing deviations from the average value of 9.8m/s2.
How is the acceleration of falling objects used in practical applications?
Understanding falling object acceleration is essential in engineering design, construction, sports, and various other fields to ensure safety, efficiency, and accuracy.
Who made significant contributions to our understanding of falling object acceleration?
Galileo Galilei and Isaac Newton played pivotal roles in advancing our knowledge of falling object acceleration through their experiments and theories.