Salary sueldo ingreso beneficio deuda: Delving into the intricacies of compensation, income generation, employee perks, and debt management, this article unravels the essential components of financial well-being.
In the realm of personal finance, understanding the concepts of salary, income, benefits, and debt is paramount. These elements intertwine to shape our financial landscape, impacting our ability to meet expenses, achieve financial goals, and secure a stable future.
Salary
Salary refers to the fixed amount of compensation paid to an employee for their work over a specific period, typically on a monthly or annual basis. It is a fundamental component of an employee’s compensation package and plays a crucial role in determining their financial well-being.
Salaries are structured differently depending on the industry, company, and employee’s position. Some common types of salaries include:
- Base salary: The fixed amount of compensation paid to an employee regardless of performance or bonuses.
- Performance-based salary: A salary that is tied to the employee’s performance and achievements, often based on metrics such as sales targets or project deliverables.
- Commission-based salary: A salary that is based on the amount of sales or services generated by the employee.
Income: Salary Sueldo Ingreso Beneficio Deuda

Income refers to the total amount of money earned by an individual or organization over a specific period, typically on a monthly or annual basis. It is a crucial factor in determining an individual’s or organization’s financial well-being and is derived from various sources.
The primary sources of income include:
- Employment income: Income earned through employment, such as salaries, wages, commissions, and bonuses.
- Investment income: Income earned from investments, such as dividends, interest, and capital gains.
- Business income: Income earned from owning and operating a business.
- Passive income: Income earned from sources that do not require active involvement, such as rental properties or royalties.
Benefits
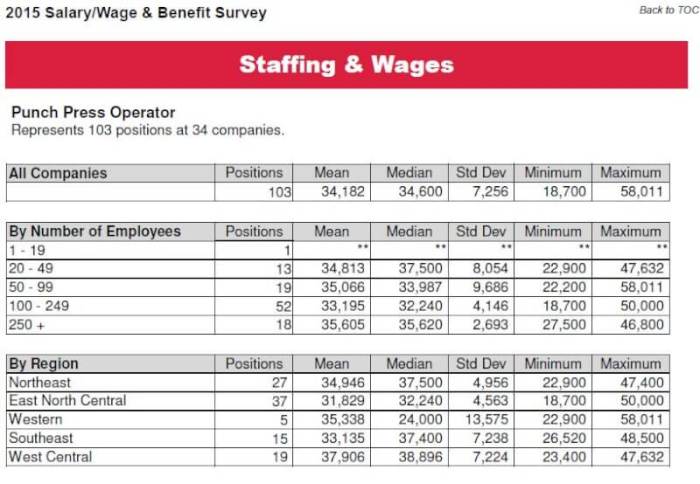
Employee benefits refer to the non-salary compensation provided to employees by their employers as part of their compensation packages. These benefits play a significant role in attracting and retaining talented employees and enhancing their overall well-being.
Common types of employee benefits include:
- Health insurance: Coverage for medical expenses, including doctor’s visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs.
- Paid time off: Time off from work with pay, including vacation days, sick days, and personal days.
- Retirement plans: Employer-sponsored plans that help employees save for retirement, such as 401(k) plans and pensions.
- Life insurance: Insurance that provides financial protection to the employee’s family in the event of their death.
Debt

Debt refers to the amount of money owed by an individual or organization to another party. It can have a significant impact on financial well-being, both positively and negatively.
Common types of debt include:
- Credit card debt: Debt incurred through the use of credit cards.
- Student loans: Debt incurred to finance higher education.
- Mortgages: Debt incurred to finance the purchase of real estate.
- Personal loans: Debt incurred for various personal expenses, such as medical bills or home renovations.
Questions and Answers
What is the difference between salary and income?
Salary refers to the fixed amount of compensation received by an employee for their work, typically paid on a regular basis. Income, on the other hand, encompasses all forms of earnings, including salary, wages, bonuses, investments, and other sources.
What are the different types of employee benefits?
Employee benefits vary widely, but common types include health insurance, paid time off, retirement plans, stock options, and educational assistance.
How can I manage debt effectively?
Effective debt management involves creating a budget, prioritizing high-interest debts, consolidating or refinancing loans, and seeking professional guidance if necessary.